Standards & Regulations for workwear
Several of our products are designed to meet with various international standards and rules in order to provide consumers with the best possible protection.
The ENGEL Workwear Safety and Safety+ lines, in particular, have several certifications. This is an area where adherence to various workplace regulations is critical, as is matching the designation and offering best protection.

Products certified to EN 342 are suitable for use in cold places when the combination of -5° C or lower air temperature, humidity, and wind increases the demand for insulating clothing.
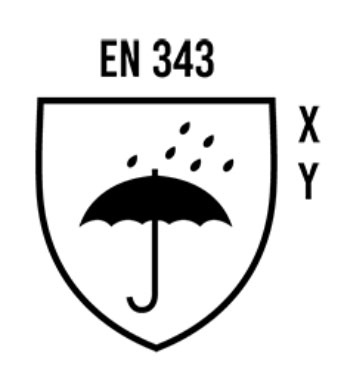
This symbol indicates the level of protection. The values next to the pictogram indicate: x: The capacity of the outdoor garment to withstand water entry from the outside (water resistance).
3 = Highest protection
1 = Lowest protection
y: Moisture transfer resistance (breathability) reflects how efficiently moisture from sweat may escape from the interior to the outside via the outer fabric.
3 = Very good drainage
1 = Poor drainage

The EN ISO 20471 standard is broken into three categories. The class label describes how effectively the product can make the person visible. The larger the area of fluorescent material and reflection, the higher the classification. The fluorescent material improves visibility in daytime and twilight, while the reflecting areas become visible in the dark when a vehicle’s or a work light is directed at the wearer.

The Railway Group Standard sets out the minimum requirements for high visibility warning garments in the rail industry.

EN ISO 11612 protective clothing protects against short-term exposure to heat and flame.
This standard is divided into multiple categories, with the code letter indicating which requirements the clothing item in question meets. Each category is further subdivided into categories based on the level of protection provided.
(A1) Limited flame spread
(A2) Edge ignition
(B) Convective heat, level class 1-3, where 3 is the highest
(C) Radiant heat, levels 1-4, where 4 is the highest
(D) Molten aluminium splash, levels 1-3, where 3 is the highest
(E) Molten iron splash, levels 1-3, where 3 is the highest
(F) Contact heat, levels 1-3, where 3 is the highest

EN ISO 11611 protective clothing protects against welding/spatter of molten metal and sparks, as well as heat in the form of convection- or radiant heat.
1 Protects against less hazardous welding techniques and situations, where limited spatter and radiant heat occur. Metal spatter 15 drops. Radiant heat 7 seconds.
(A1) Limited flame spread
2 Protects against more hazardous welding techniques and situations where there is greater spatter and radiant heat. Metal spatter 25 drops. Radiant heat 16 seconds.
(A2) Limited flame spread, edge ignition

Anti-static protective apparel. This garment guards against electrostatic discharges when static sparks might ignite flammable or explosive atmospheres.
The user must be properly earthed, such as by wearing appropriate footwear, and garments must be attached to the body.

EN 61482-1-2 protective apparel guards against thermal risks from an electric arc. According to this standard, such apparel provides protection against electric arcs and is classified into two types.
Class 1 Protection against electric arc 4kA
Class 2 Protection against electric arc 7kA

Protective clothing in accordance with EN 13034-6 protects against liquid chemical splashes and is intended for use in cases involving a sufficiently low risk assessment and when a complete protective barrier against liquids is not required, i.e. when the user is able to react in time when his or her clothing has become contaminated. Potential exposure to modest volumes of spray or periodic low-volume splashes may provide a minimal danger.
The product has been tested for the following chemicals:
- Sulphuric acid 30% solution
- Caustic soda 10% solution
- Dimethylbenzene
- Xylol
- Butanol-1
- Phosphoric acid 10% solution
EN ISO 13688
General requirements for protective clothing.
